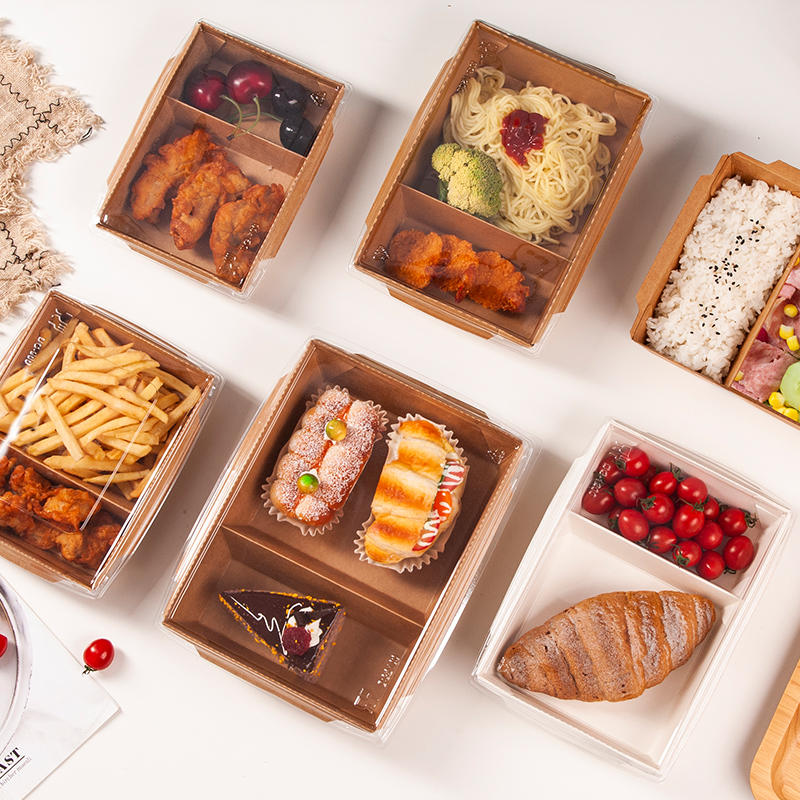
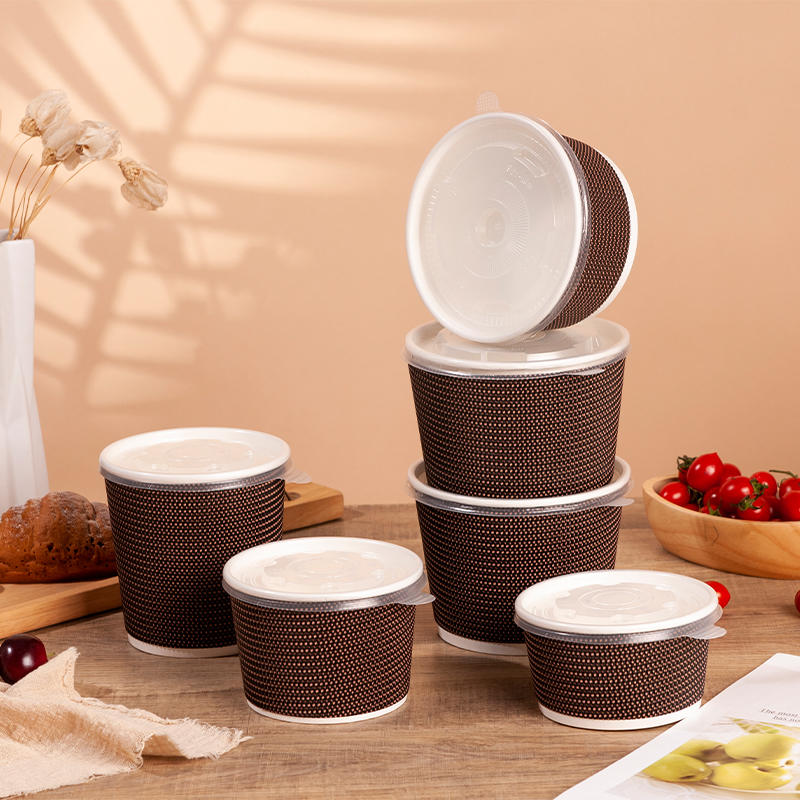
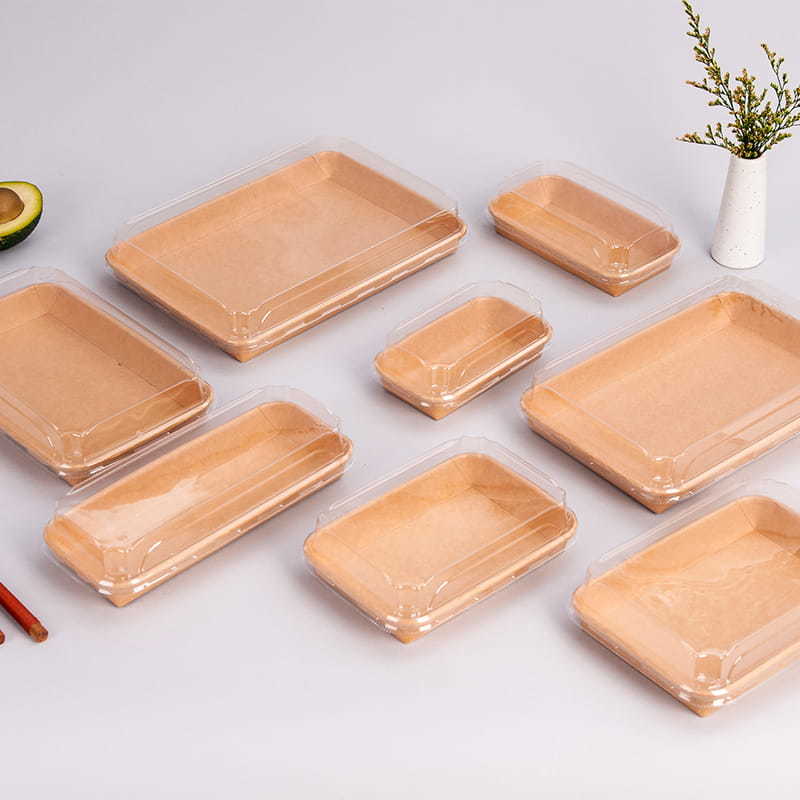
Material Selection:
Moisture Resistance: Packaging materials with inherent moisture resistance, such as certain types of plastics (e.g., polyethylene, polypropylene), laminates, and coated papers, are chosen to prevent moisture absorption and ingress. Additionally, moisture-resistant coatings or barrier layers can be applied to paper-based packaging to enhance its resistance to humidity and moisture.
Heat Resistance: Heat-resistant materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polypropylene (PP), and certain types of plastics and laminates are selected for packaging applications where exposure to high temperatures is expected, such as microwaveable food packaging or hot-fill applications. These materials maintain their structural integrity and barrier properties when subjected to heat.
Other Environmental Factors: Packaging materials are also chosen based on their resistance to other environmental factors, such as light exposure (UV resistance), oxygen permeation (oxygen barrier properties), and mechanical stress (tear resistance, puncture resistance). Materials that offer robust performance under various environmental conditions are preferred to ensure the integrity and functionality of the packaging.
Barrier Properties:
Food packaging boxes structures are designed to provide effective barriers against moisture, oxygen, light, and other environmental factors that can compromise the quality and shelf life of food products. Multilayer constructions, including barrier films, metallized layers, and coatings, are employed to enhance barrier properties and protect the contents from external influences.
Barrier performance can be further optimized through the use of specialized barrier additives, such as ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) or aluminum oxide nanoparticles, which are incorporated into the packaging materials to improve resistance to moisture, oxygen, and other gases.
Sealing and Closure Systems:
Secure sealing and closure systems are essential for preventing moisture ingress, heat loss, and contamination. Packaging boxes are equipped with effective sealing mechanisms, such as heat seals, adhesive closures, zip-lock features, or tamper-evident seals, to create airtight and moisture-resistant enclosures.
Advanced sealing technologies, including induction sealing and ultrasonic sealing, are employed to achieve strong, hermetic seals that withstand environmental stresses and maintain product freshness and integrity.
Testing and Quality Assurance:
Packaging materials and structures undergo rigorous testing to assess their resistance to moisture, heat, and other environmental factors. Various testing methods, such as moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) testing, heat resistance testing, and accelerated aging tests, are conducted to evaluate the performance of packaging materials under simulated environmental conditions.
Quality assurance measures, including regular audits, inspections, and quality control protocols, are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that packaging boxes meet specified performance criteria and comply with regulatory requirements.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体













