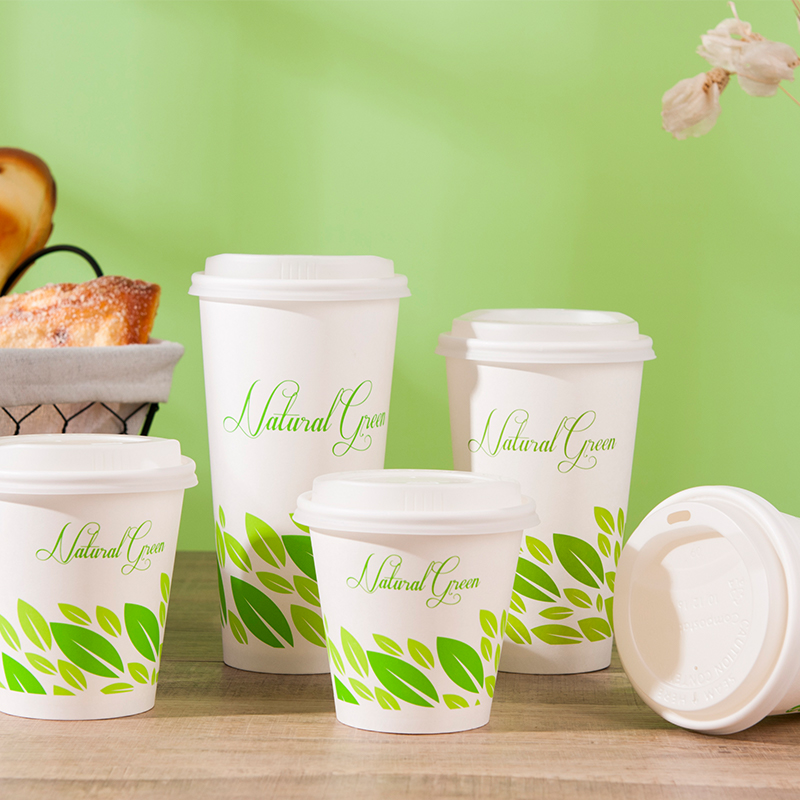
The blending of functionality with sustainability in paper cup design and manufacturing involves a holistic approach that considers various aspects of the product's life cycle. Here's how the design and manufacturing of paper cups strive to achieve this balance:
1. Material Selection:
Functionality: Paper cups are primarily made from paperboard, providing a lightweight and convenient option for beverage consumption.
Sustainability: Manufacturers choose materials from responsibly managed forests and consider options with Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification to ensure sustainable sourcing.
2. Biodegradability and Compostability:
Functionality: Paper cups are designed to be functional for holding hot and cold beverages.
Sustainability: Some paper cups are made to be biodegradable or compostable, allowing them to break down naturally and reduce their environmental impact.
3. Recyclability:
Functionality: Paper cups are designed to be sturdy and reliable for single-use purposes.
Sustainability: Efforts are made to design cups that are easily recyclable, contributing to a circular economy by reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency.
4. Water-Based Inks and Coatings:
Functionality: Cups are often printed with branding, logos, or designs to enhance their visual appeal.
Sustainability: Water-based inks and coatings are used for printing, reducing the environmental impact compared to solvent-based options.
5. Reduced Material Thickness:
Functionality: Paper cups are designed to provide insulation and prevent heat transfer for hot beverages.
Sustainability: Innovations aim to reduce material thickness without compromising functionality, leading to resource efficiency and less environmental impact.
6. Certifications for Sustainable Practices:
Functionality: Paper cups adhere to health and safety regulations for food contact materials.
Sustainability: Seeking certifications such as FSC ensures that the manufacturing process aligns with sustainable forestry practices.
7. Consumer Education:
Functionality: Cups are designed for easy use and disposal.
Sustainability: Consumer education is crucial to inform users about the importance of proper disposal methods and the environmental benefits of choosing sustainable options.
8. Lifecycle Analysis:
Functionality: Paper cups are designed for a specific lifespan of single use.
Sustainability: Lifecycle analyses are conducted to assess the overall environmental impact, guiding improvements in raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life considerations.
9. Innovative Designs:
Functionality: Ongoing innovation addresses user needs, such as spill-resistant lids and ergonomic designs.
Sustainability: Innovation explores new materials, coatings, and production techniques to enhance sustainability without compromising functionality.
10. Continuous Improvement:
Functionality: Regular improvements address durability, insulation, and user experience.
Sustainability: Continuous improvement efforts focus on reducing the environmental footprint through more sustainable materials and practices.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体













